Market
Summary
Market is a contract to define tokenization scheme in Dev Protocol, and is defined on the basis of users’ suggestions.
Developers of Market can develop or deploy smart contracts based on MarketBehavior interface, and add Markets at vote queue through MarketFactory contracts. Voting becomes open to staking users by govern.devprotocol.xyz. Once voting is approved, Market is activated by DAO maintainer or keepers.
Market has 2 functions:
- Authentication: Based on the arguments given by users, Market verifies whether the users are appropriate certificate holders.
- Deauthentication: Based on users’ request, authenticated information is deleted.
Developers of Market can only define the process of authentication in these functions.
Market defines types of activities that can be expressed by Property tokens The following figure shows the relation between Market and Property tokens.
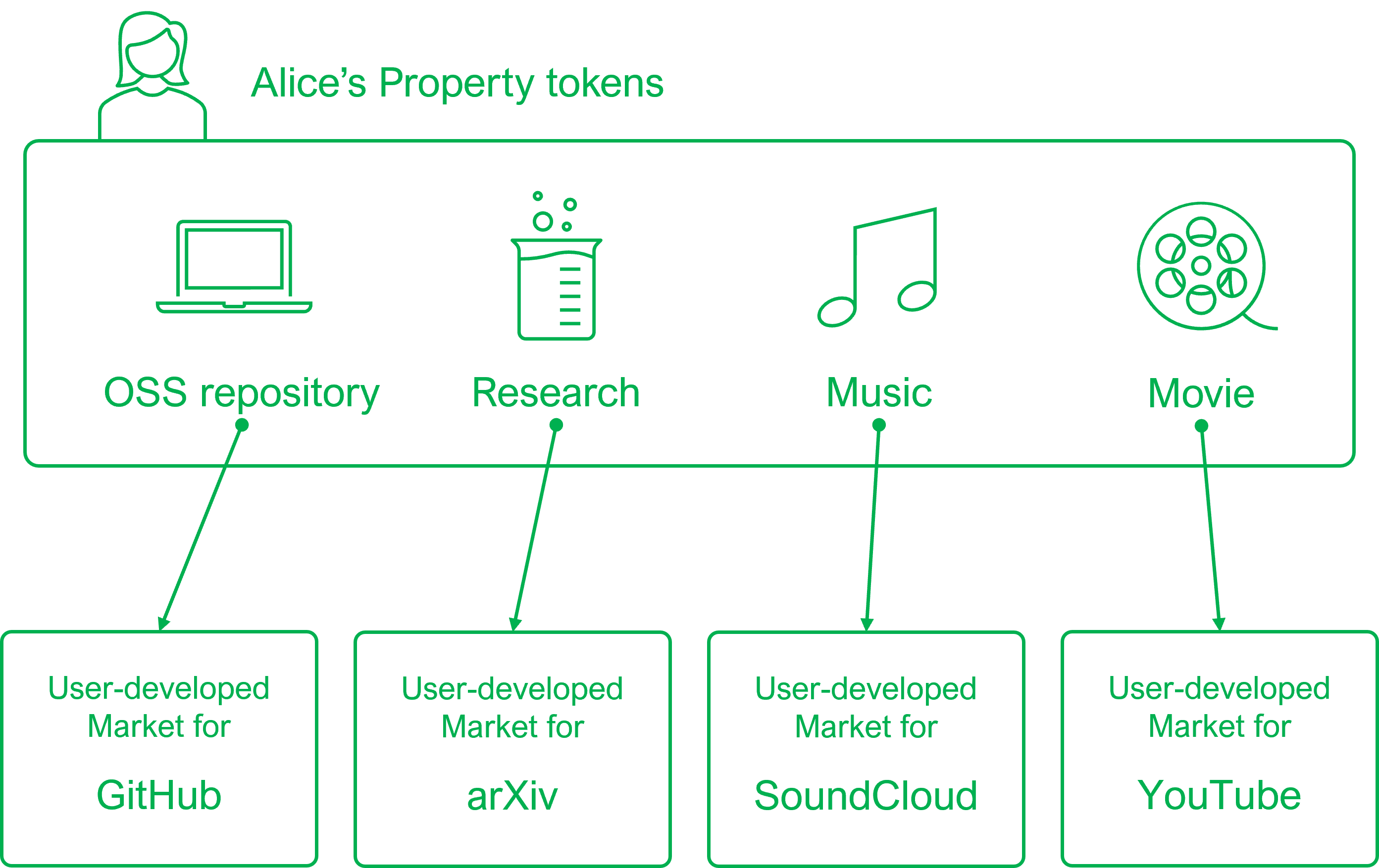
Activation of Market
1 - Development
Developers of Market need to develop smart contracts in accordance with MarketBehavior interface.
2 - Deploy
Developers deploy Market contract that they developed. Smart contracts to deploy are the contracts that succeeded MarketBehavior interface and their dependence.
3 - MarketFactory
After developers call MarketFactory.create, MarketFactory automatically generates Market contract that incorporates Market developed by users.
4 - Vote
Developers request Dev Protocol DAO to judge whether automatically generated Market contracts should be activated.
In the future, we're hoping that voting contract would be deployed at the same time of executing
MarketFactory.create, although users need to create voting contracts currently. Voting contracts can be created with VoteFactory contracts.
Contract: https://github.com/dev-protocol/vote-governance/blob/main/contracts/VoteFactory.sol
Mainnet: https://etherscan.io/address/0x36199cb1e12c5b9d5a203f9dcb53b37e3ca6a30f
Sample tx: Ethereum Transaction Hash (Txhash) Details | Etherscan
5 - Activation
After the vote is approved, automatically generated Market contracts are activated by DAO maintainers or keepers.
In the future, we're hoping that this process would be automated by keepers, although it is activated by multisig of several DAO members.
Interface
Developers of Market need to develop smart contracts in accordance with MarketBehavior interface.
Interface is as follows:
https://github.com/dev-protocol/protocol/blob/main/contracts/interface/IMarketBehavior.sol
interface IMarketBehavior {
function authenticate(
address _prop,
string calldata _args1,
string calldata _args2,
string calldata _args3,
string calldata _args4,
string calldata _args5,
address market,
address account
) external returns (bool);
function schema() external view returns (string memory);
function getId(address _metrics) external view returns (string memory);
function getMetrics(string calldata _id) external view returns (address);
}
Smart contracts developed with a basis of MarketBehavior will be called by Market contracts generated through MarketFactory.create.
Authentication
When end users call Market.authenticate, MarketBehavior.authenticate will be called. Only when Market.authenticate executes the validations below and pass them all, it calls MarketBehavior.authenticate. Therefore, the following validations are unnecessary for the implementation of MarketBehvaior.authenticate.
- The caller is an author of the first argument Property.
- The second argument is not empty.
The interface of Market.authenticate is as follows:
function authenticate(
address _prop,
string calldata _args1,
string calldata _args2,
string calldata _args3,
string calldata _args4,
string calldata _args5
) external returns (bool);
The interface of MarketBehavior.authenticate is as follows:
function authenticate(
address _prop,
string calldata _args1,
string calldata _args2,
string calldata _args3,
string calldata _args4,
string calldata _args5,
address market,
address account
) external returns (bool);
_prop: address of Property tokens that are targets for authentication._args1: asset ID to authenticate._args2~5: additional information to be used for authentication.market: Market address that called MarketBehavior.account: caller's address at Market.
Basically, MarketBehavior executes authentication based on the free information from _args1 to _args5, and then it defines what MarketBehavior is expecting to get for the arguments at MarketBehavior.schema.
Here's an example for MarketBehavior.schema:
["GitHub Repository (e.g, your/awesome-repos)", "Khaos Public Signature"]
This schema shows us that _args1 is GitHub repository name, _args2 is Khaos Public Signature, and the rest is empty.
Authentication logic of MarketBehavior depends on developers. They need to call Market.authenticateCallback to show the success of authentication. Market address as callee will be the address of argument market.
The interface of Market.authenticatedCallback is as follows:
function authenticatedCallback(address _property, bytes32 _idHash)
external
returns (address);
For the first argument, you'll pass through the first argument of MarketBehavior.authenticate. For the second argument, you'll use hashed value of the first argument of MarketBehavior.authenticate.
In the case where authentication logic of MarketBehavior is only synchronous processing, it's easy to pass through arguments, although in many cases, we need asynchronous processing. In the case of authentication logic with asynchronous processing, we suggest you temporarily save the value at local variables of MarketBehavior as shown below.
contract GitHubMarket is IMarketBehavior {
address private khaos;
mapping(address => string) private repositories;
mapping(bytes32 => address) private metrics;
mapping(bytes32 => address) private properties;
mapping(bytes32 => address) private markets;
mapping(bytes32 => bool) private pendingAuthentication;
mapping(string => bool) private publicSignatures;
constructor(address _khaos) public {
khaos = _khaos;
}
function authenticate(
address _prop,
string memory _githubRepository,
string memory _publicSignature,
string memory,
string memory,
string memory,
address _dest,
address account
) external override whenNotPaused returns (bool) {
bytes32 key = createKey(_githubRepository);
properties[key] = _prop;
markets[key] = _dest;
pendingAuthentication[key] = true;
return true;
}
function khaosCallback(
string memory _githubRepository,
uint256 _status,
string memory _message
) external whenNotPaused {
require(msg.sender == khaos, "illegal access");
require(_status == 0, _message);
bytes32 key = createKey(_githubRepository);
require(pendingAuthentication[key], "not while pending");
register(key, _githubRepository, markets[key], properties[key]);
}
function register(
bytes32 _key,
string memory _repository,
address _market,
address _property
) private {
address _metrics = IMarket(_market).authenticatedCallback(
_property,
_key
);
repositories[_metrics] = _repository;
metrics[_key] = _metrics;
}
function createKey(string memory _repository)
private
pure
returns (bytes32)
{
return keccak256(abi.encodePacked(_repository));
}
function schema() external override view returns (string memory) {
return
'["GitHub Repository (e.g, your/awesome-repos)", "Khaos Public Signature"]';
}
function getId(address _metrics)
external
override
view
returns (string memory)
{
return repositories[_metrics];
}
function getMetrics(string memory _repository)
external
override
view
returns (address)
{
return metrics[createKey(_repository)];
}
}
Deauthentication
When users call Market.deauthenticate, information for authentication designated by users will be deleted. Since the implementation of Market.deauthenticate doesn't depend on MarketBehavior, developers of Market doesn’t need to implement it.